

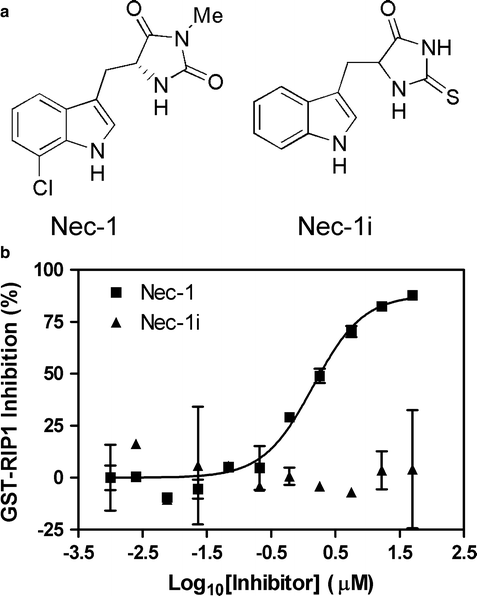
Gonzalez FJ, Gelboin HV (1992) Human cytochromes P450: evolution and cDNA-directed expression. Grimm SW et al (2009) The conduct of in vitro studies to address time-dependent inhibition of drug-metabolizing enzymes: a perspective of the pharmaceutical research and manufacturers of America. Here we describe both dilution and non-dilution methods to evaluate the time-dependent inhibition against CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4 (midazolam and testosterone as substrate) in human liver microsomes. In the non-diluted method, there is no dilution step between the preincubation and the incubation, and a lower concentration of HLMs can be used throughout the experiment.
In the dilution method, the compound is preincubated for 30 min with a relatively higher concentration of HLMs (with and without NADPH), and the samples are diluted ten-fold before measuring CYP enzyme activity. There are two main methods to assess the IC50 shift, dilution method, and non-dilution method. TDI is usually studied by measuring the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) shift of a drug candidate after a 30-min incubation with human liver microsomes (HLMs) in the presence and absence of NADPH. Evaluation of the time-dependent inhibition (TDI) of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes is very important for understanding the drug–drug interactions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
